PROVEN RESULTS
Jump to topic:
Rebif® was proven effective in a clinical study vs placebo
When compared to placebo, Rebif® was proven effective in treating relapsing multiple sclerosis (RMS) in 3 important ways.
Slowed the time to disability progression
Showed fewer relapses
Showed fewer new or enlarging magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain lesions*†
This was shown in a placebo-controlled study of Rebif® for RMS called PRISMS.‡ The 2-year PRISMS study looked at 560 people to see how they responded. 189 people took Rebif® 22 mcg, 184 took Rebif® 44 mcg, and 187 took a placebo, all given under the skin 3 times a week.
*Lesions detected with both T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced (T1-Gd+) and T2-weighted MRI.
†Refers to new lesions and total lesion burden or area as defined in the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and MS Council guidelines.
‡Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon β-1a Subcutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis.


The overall results for people taking Rebif® 44 mcg showed:
*Gadolinium is a contrast medium injected prior to MRI scans. It passes through breaches in the blood-brain barrier and is therefore used to highlight new and active lesions. The usage of gadolinium greatly enhances the sensitivity of a T1-weighted MRI.
†Lesions detected with both T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced (T1-Gd+) and T2-weighted MRI.
‡Refers to new lesions and total lesion burden or area as defined in the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and MS Council guidelines.
§From a subgroup of 134 patients in the PRISMS study who received 11 consecutive monthly T2- and T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced MRI scans beginning 1 month before treatment initiation.
||Median number of lesions, per patient per scan, based on comparisons from rank-based analysis of variance (ANOVA). Lesions detected with both T1-Gd+ and T2-weighted MRI. Median = a value in an ordered set that has an equal number of values higher and lower.
¶The number of lesions represents new or enlarging lesions, per patient per scan.
#Disability progression was defined as an increase of at least 1 point in the EDSS that was sustained for at least 3 months.


Rebif showed significant results at year 2* for people with greater levels of disability
People in the PRISMS study had a range of disability at the beginning of the study. Rebif® was also shown to be effective vs placebo for a subset of people who started taking Rebif® and had greater disability (scores of 3.5 to 5.0 on the EDSS).
Expanded Disability Status Scale and Disability Progression
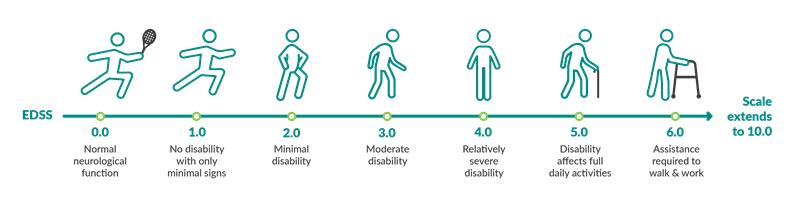
*Disability progression was defined in a Rebif® clinical trial as an increase of at least 1 point on the EDSS that was sustained for at least 3 months.
In this subset of people with greater disability at the beginning of the study, 31 people took Rebif® 44 mcg 3 times a week under the skin, and 28 people took a placebo.
*Disability progression was defined as an increase of at least 1 point in the EDSS that was sustained for at least 3 months.
†Lesions detected with both T1-Gd+ and T2-weighted MRI.
‡Refers to new lesions and total lesion burden or area as defined in the AAN and MS Council guidelines.
§Based on comparisons from rank-based ANOVA.
||Median = a value in an ordered set that has an equal number of values higher and lower.


Most common side effects seen in the PRISMS study
Injection site reactions (92% and 89% vs 39%)
Headache (70% and 65% vs 63%)
Influenza-like symptoms (59% and 56% vs 51%)
Leukopenia (36% and 28% vs 14%)
Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase increased (27% and 20% vs 4%)
Abdominal pain (20% and 22% vs 17%)
Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase increased (17% and 10% vs 4%)
HEAD-TO-HEAD STUDY
Rebif® was proven superior to another relapsing MS treatment
Rebif® was compared to Avonex® in a head-to-head study called EVIDENCE.* For an average of 64 weeks, Rebif® 44 mcg was given to 339 people 3 times a week under the skin, with injections at least 48 hours apart. Avonex® 30 mcg was given to 338 people once a week into the muscle.
In this head-to-head study, high-dose, high-frequency Rebif® was proven superior to low-dose, low-frequency Avonex®† in 2 important ways:
Relapses
More people on Rebif® remained free from relapses‡
MRI lesions
More people on Rebif® showed no new or enlarging T2-brain lesions‡
More people on Rebif® were free of active, inflamed T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced§ lesions
If you’re currently on Avonex® and not doing as well as you expected or you’re considering an interferon therapy, talk to your doctor about Rebif®.
*The EVIDENCE (EVidence of Interferon Dose-response: European North American Comparative Efficacy) trial was conducted entirely in North America and Western Europe.
†The approved Avonex® dose is 30 mcg per week.
‡Lesions detected with both T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced and PD/T2-weighted MRI.
§Gadolinium is a contrast medium injected prior to MRI scans. It passes through breaches in the blood-brain barrier and is therefore used to highlight new and active lesions. The usage of gadolinium greatly enhances the sensitivity of a T1-weighted MRI.
Rebif® further reduced relapses after the head-to-head phase of the study ended
At the end of the head-to-head phase of the EVIDENCE study, the 605 remaining people were asked if they wanted to leave the study or keep going in the extension phase. In this phase of the study, which lasted an average of 8 months, 495 people chose to participate; 73% of those taking Avonex® 30 mcg once weekly chose to take Rebif® 44 mcg three times weekly, whereas 91% of those taking Rebif® 44 mcg three times weekly decided to stay with it.
Patients who started on Avonex® then moved to Rebif®
additional reduction in relapses
64% annualized relapse rate for Avonex® at the end of the head-to-head phase
32% annualized relapse rate after moving to Rebif® at the end of the extension phase*
*Average of 8 months on treatment with Rebif®
Transitioned from Avonex® to Rebif®, n=223
Patients who started on Rebif® and continued on Rebif®
additional reduction in relapses
46% annualized relapse rate for Rebif® at the end of the head-to-head phase
34% relapse rate after continuing on Rebif® at the end of the extension phase*
*Average of 8 additional months on treatment with Rebif®
Continued with Rebif®, n=272


| Side effects | % of people taking Rebif® 44 mcg three times weekly | % of people taking Avonex® 30 mcg once weekly |
|---|---|---|
| Flu-like symptoms | 45% | 53% |
| Injection site reactions | 85% | 33% |
| Liver disorders | 18% | 10% |
| White blood cell disorders | 14% | 5% |
Represents adverse events reported over an average of 64 weeks.
Avonex® is a registered trademark of Biogen.


IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATION
Important Safety Information
Do not take Rebif if you are allergic to interferon beta, human albumin, or any of the ingredients in Rebif.
Rebif can cause serious side effects. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms listed below while taking Rebif.
- Behavioral health problems including depression and suicidal thoughts. You may have mood problems including depression (feeling hopeless or feeling bad about yourself), and thoughts of hurting yourself or suicide.
- Liver problems or worsening of liver problems including liver failure. Symptoms may include nausea, loss of appetite, tiredness, dark colored urine and pale stools, yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eye, bleeding more easily than normal, confusion, and sleepiness. During your treatment with Rebif you will need to see your healthcare provider regularly and have regular blood tests to check for side effects.
- Serious allergic and skin reactions. Symptoms may include itching, swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue or throat, trouble breathing, anxiousness, feeling faint, skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or skin blisters and peels.
- Injection site problems. Rebif may cause redness, pain, itching or swelling at the place where your injection was given. Call your healthcare provider right away if an injection site becomes swollen and painful or the area looks infected. You may have a skin infection or an area of severe skin damage (necrosis) requiring treatment by a healthcare provider.
- Blood problems. Rebif can affect your bone marrow and cause low red and white blood cell and platelet counts. In some people, these blood cell counts may fall to dangerously low levels. If your blood cell counts become very low, you can get infections and problems with bleeding and bruising. Your healthcare provider may ask you to have regular blood tests to check for blood problems.
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulmonary arterial hypertension can occur with interferon beta products, including Rebif. Symptoms may include new or increasing fatigue or shortness of breath. Contact your healthcare provider right away if you develop these symptoms.
- Seizures. Some people have had seizures while taking Rebif.
Before you take Rebif, tell your healthcare provider if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
- mental illness, including depression and suicidal behavior
- liver problems
- bleeding problems or blood clots
- low blood cell counts
- seizures (epilepsy)
- thyroid problems
- drink alcohol
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Rebif will harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider if you become pregnant during your treatment with Rebif
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Rebif may pass into your breastmilk. Talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take Rebif
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
The most common side effects of Rebif include:
- flu-like symptoms. You may have flu-like symptoms when you first start taking Rebif. You may be able to manage these flu-like symptoms by taking over-the-counter pain and fever reducers. For many people, these symptoms lessen or go away over time. Symptoms may include muscle aches, fever, tiredness, and chills
- stomach pain
- change in liver blood tests
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Rebif. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or visit www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Indication
Rebif® (interferon beta-1a) is a prescription medicine used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. It is not known if Rebif is safe and effective in children.
Please see Rebif® Prescribing Information and Medication Guide.
