The people in these photos are not actual Rebif® patients.
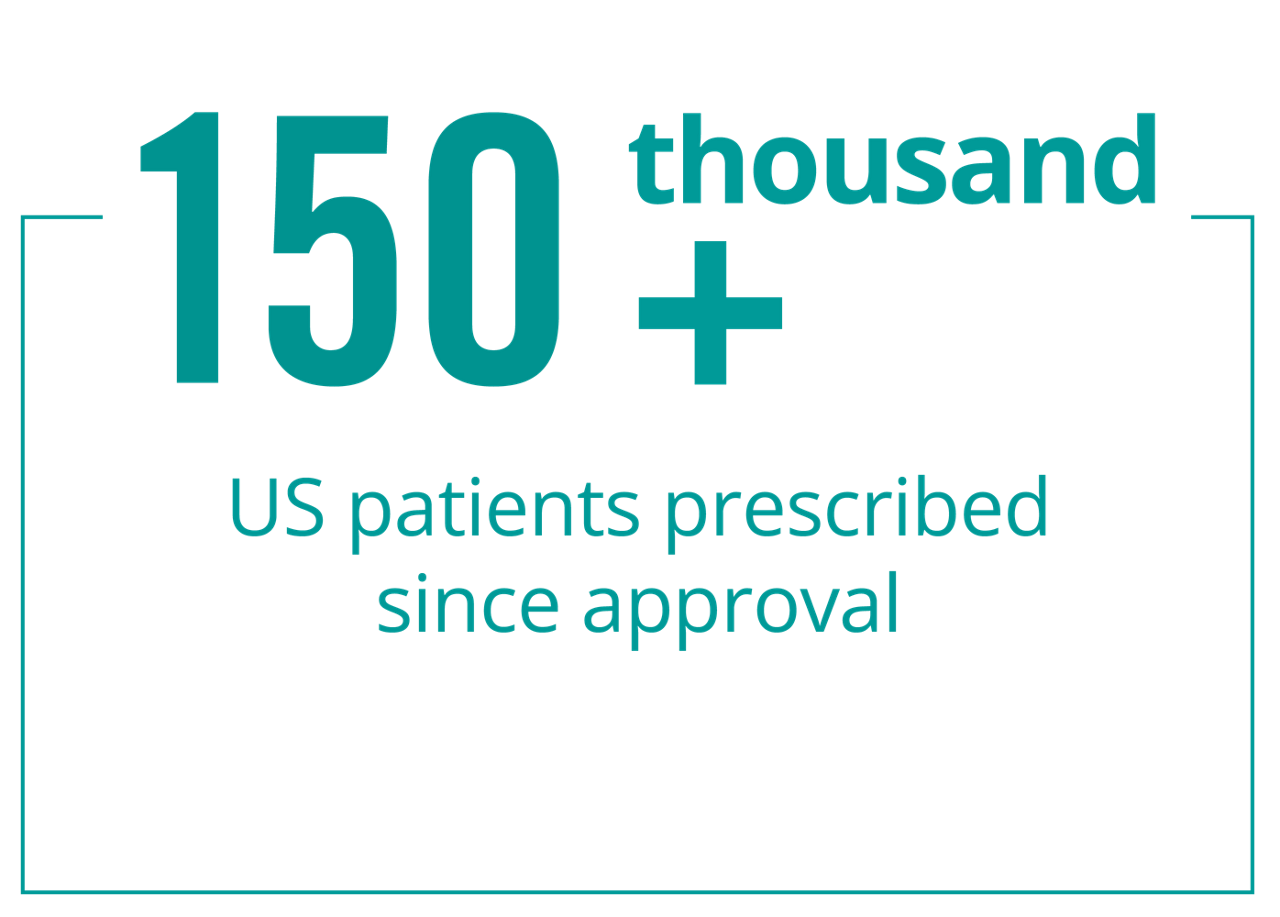
The well-established safety profile of Rebif® is supported by more than 20 years of combined clinical trial data and real-world patient experience. Safety is an important topic to discuss with your healthcare provider when choosing a relapsing multiple sclerosis (RMS) treatment.
Rebif® is an immunomodulator, a medication used to help regulate the immune system. It doesn’t continuously suppress your immune system.
Rebif® can cause serious side effects. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms listed below while taking Rebif®.
Behavioral health problems, including depression and suicidal thoughts. You may have mood problems including depression (feeling hopeless or feeling bad about yourself), and thoughts of hurting yourself or suicide.
Liver problems or worsening of liver problems, including liver failure. Symptoms may include nausea, loss of appetite, tiredness, dark colored urine and pale stools, yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eye, bleeding more easily than normal, confusion, and sleepiness. During your treatment with Rebif® you will need to see your healthcare provider regularly and have regular blood tests to check for side effects.
Serious allergic and skin reactions. Symptoms may include itching, swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue or throat, trouble breathing, anxiousness, feeling faint, skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or skin blisters and peels.
Injection site problems. Rebif may cause redness, pain, itching or swelling at the place where your injection was given. Call your healthcare provider right away if an injection site becomes swollen and painful or the area looks infected. You may have a skin infection or an area of severe skin damage (necrosis) requiring treatment by a healthcare provider.
Seizures. Some people have had seizures while taking Rebif.®
Flu-like symptoms (see below for more details)
Stomach pain
Change in liver blood tests
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
For more information, please see the additional Important Safety Information, full Rebif Prescribing Information, and Medication Guide.
Flu-like symptoms are one of the most common side effects of Rebif®. These can range from fever, chills, and sweating to muscle aches and tiredness. These symptoms are not actually flu, and they are not caused by a viral infection—nor do they include vomiting and diarrhea. For many people, these symptoms lessen or go away over time.
If you have questions or your symptoms are concerning, talk to your healthcare provider. Here are some steps you can take that may help you manage flu-like symptoms:
Consider taking an over-the-counter pain reliever/fever reducer as directed by your healthcare provider. These are medicines that you can buy at your local pharmacy without a prescription. They may also have their own side effects, so read the instructions carefully. Talk to your healthcare provider or an MS LifeLines® Nurse for more information
Find a time of day that works for you to take your Rebif®. Some people inject Rebif® around bedtime to help them sleep through some flu-like symptoms they may have. Others find that injecting earlier in the day works best for them. Remember, Rebif® should be taken on the same 3 days a week—for example, Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Your injections should be at least 48 hours apart. Take injections at the same time each day
Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about titration when first starting on Rebif®. Titration means starting at a lower dose and then gradually building up to the full dose. This may help reduce flu-like symptoms when you're first starting on Rebif®.
Please see Important Safety Information below and the Rebif® Medication Guide and Prescribing Information at the top of this page. Speak with your healthcare provider for more information or about any side effects that you may have.
Rebif® may cause redness, pain, or swelling at the place where an injection was given. Some patients have developed skin infections or areas of severe skin damage (necrosis), requiring treatment by a doctor. If one of your injection sites becomes swollen and painful or the area looks infected, you should call your healthcare provider right away.
Here is some information that may help you with injection site discomfort:
Bring the syringe to room temperature. Removing the syringe from your refrigerator 1 to 4 hours before injecting may help to reduce irritation. Keep in mind that Rebif® syringes should never be warmed in a microwave or placed in boiling water
Clean your injection site beforehand with alcohol swabs. Allow the area to dry before injecting to reduce irritation
Rotate your injection sites! Be sure to rotate your site each time, and don't reuse the same injection spot for at least 7 days. Your treatment tracker can help you to keep track of your injections. Download your own treatment tracker
Apply a cold compress or ice pack to the injection site after injection; this may help reduce local skin reactions
Monitor your injection site over several days for redness, swelling, or tenderness
The people in these photos are not actual Rebif® patients.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATION
Important Safety Information
Do not take Rebif if you are allergic to interferon beta, human albumin, or any of the ingredients in Rebif.
Rebif can cause serious side effects. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms listed below while taking Rebif.
Before you take Rebif, tell your healthcare provider if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
The most common side effects of Rebif include:
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Rebif. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or visit www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Indication
Rebif® (interferon beta-1a) is a prescription medicine used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. It is not known if Rebif is safe and effective in children.
Please see Rebif® Prescribing Information and Medication Guide.